Targeted marketing is the strategy of identifying an audience’s interests to optimize the organization’s chances of success. Whether one’s business is a start-up, a multinational company or an individual business, the key to successful marketing is determining and reaching the correct audience.
This extensive article will use different ideas and illustrations to explain target audiences and the best ways to identify prospective consumers to market to.
What Is A Target Audience?
A target audience refers to a particular consumer market that the organization has chosen as the most appropriate audience for a particular marketing message or the organization’s goods and services. These people have similar traits, requirements, and actions toward the same catchy product or service that attracts their attention.
The concept is useful in that it relieves a business organization from doing all things to all people by indicating that marketing strategies, communication efforts and products should be geared toward specific groups most likely to respond favorably to the business organization’s efforts.

Key Components of Target Audience
Demographics
Demographics are the quantitative measures of the people’s characteristics in a particular society, nation or country. When defining a target audience, key demographic factors include:
- Age
- Gender
- Income level
- Education
- Occupation
- Marital status
- Family size
- Ethnicity
- Religion
A luxury watch can be marketed as a status symbol to a selected group of customers, such as successful businessmen and managers aged between 35 and 55, with high purchasing capabilities as well as good taste for refined accessories.
Attitudes and Opinions
This knowledge will help in the programming and management of the stations. It can also assist in creating targeted messages and products related to the intended audience’s beliefs, values, and opinions. This includes:
- Political views
- Environmental concerns
- Social issues
- Brand preferences
- Lifestyle choices
Example:
Sustainable clothing companies might want to reach out to consumers who are conscious of the social and natural environment.
Behaviors
Behavioral factors focus on how your target audience acts in relation to your product or service. This includes:
- Purchasing habits
- Brand loyalty
- Usage patterns
- Decision-making processes
- Online vs. offline shopping preferences
Example
An example of this would be a mobile gaming firm selecting a demographic that uses their phones often and plays games on the go during their daily commute.
Needs
Identifying the specific needs of your target audience is crucial for product development and marketing:
- Pain points
- Desires
- Unmet market gaps
- Convenience factors
- Emotional needs
Example
A relaxation app may provide ways to minimize stress for working people who experience stress in their daily occupations.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle factors refer to aspects of your target population’s daily life and occupation. This includes:
- Hobbies and interests
- Social activities
- Work-life balance
- Travel habits
- Health and fitness routines
Example
You might run a fitness equipment manufacturing company that produces premium equipment. You may want to reach business people and other professionals who prefer home sessions rather than visiting the gym several times a week.
Interests
The insight about your audience is useful in developing good content and products within the market. This includes:
- Favourite media (TV shows, movies, books)
- Sports and recreation
- Arts and Culture
- Technology preferences
- Food and dining preferences
Example
An example of this might be a cooking subscription box service, which might appeal to the customer base of foodies who like to try new things.
Psychographics
Psychographic factors delve into the psychological aspects of your target audience, including:
- Personality traits
- Values and beliefs
- Aspirations and goals
- Fears and challenges
- Motivations
Example:
A personal development course might be directed towards people who are motivated, proactive, and eager to enhance their specific or general carrying capacity.
Location
Geographic factors can play a crucial role in defining your target audience:
- Country
- Region
- Urban vs. rural
- Climate
- Cultural norms specific to the area
Example:
A consumer may be interested in specific products, such as winter wear; hence, an appropriate clothing company should target consumers in cold-climate areas or countries that experience cooler seasons.

Types of Target Audience
It is also important to look at the differences between the various kinds of target public to be able to market correctly. Let’s explore each type in detail:
1. Demography
- Age: It is understood that people of different ages vary in terms of their wants, conduct and behaviours. For example, products targeting teenagers will differ from those targeting seniors.
- Gender: It can easily be observed that specific commodities or services may be preferred by either the male or female gender. There is truth in the saying that the way to the heart is through the stomach; awareness of gender predispositions is useful in developing more compelling advertising appeals.
- Income: Purchasing power is one of the main determinants, which is affected by the income levels of a particular country and, hence, the products that consumers can afford. Income consumers may purchase luxury products, while low-income consumers may be interested in cheap products.
- Education: It is very important to understand that one’s educational background plays a significant role in determining an individual’s interests, preferences, and decisions. Some products associated with the area, like intellectual or professional, and might interest highly educated persons.
- Occupation: Careers define lifestyles and, therefore, consumer behaviour. Experts in different occupations may require different things, like formal wear for business-oriented people or certain technology-related gadgets.
- Marital Status: The existence of households whereby life status is a factor that determines their purchases was also mentioned. In the past and present, the market has different target groups, which are singles, married couples, and families with different needs and spending abilities.
- Family Size: Relating to this, the size of families influences the buying requirements and expenses. Thus, for instance, while the big families might be concerned with buying goods in bulk and offers, the small families may care more for the quality of goods.
Example: A baby product company might target new parents aged 25-35 with middle to high incomes. This demographic is likely to have the financial means to spend on quality baby products and the motivation to invest in items that ensure the well-being and comfort of their children.
By understanding this demographic’s specific needs and preferences, the company can tailor its marketing messages, product offerings, and promotional strategies to effectively reach and engage this group.
2. Lifestyle
Life stance targeting looks at how a person goes about his/her daily business, the look that he/she has and the outlook on life. Key factors include:
- Hobbies and Interests: Regarding recreational activities, it becomes easier to market products to people or even market them on certain occasions. For instance, outdoor equipment manufacturers’ audience is hikers.
- Social Activities: Focus areas can be determined by defining peoples’ social preferences, such as concerts, restaurants, or community activities that would help in promotions and partnerships with specific events or restaurants.
- Work-Life Balance: Realizing how consumers balance their lives at work enables brands to meet their needs proficiently. Business people may find some of the products easy to use and take advantage of products that save time.
- Leisure Preferences: Understanding the nature of people’s free time and how they like to engage themselves when they are not working on a commodity enables the creation of products that fit these leisure activities, such as touring, reading or gaming.
- Health and Fitness Habits: Segmenting people based on their commitment to their health in the health and fitness industry can be vital to all companies. Lifestyle presents itself well for this audience, as it tries to provide products associated with an active lifestyle.
- Dining and Entertainment Choices: Information collected on consumers’ perspectives on dining habits and entertainment helps brands to target consumers according to their tastes in eating out and forms of entertainment.
Example: A yoga apparel brand will likely target people who are conscious of their health and consider exercising often. The identified audience can be characterized as active, physically healthy, and attentive to their physical and mental condition, thus confirming their desire to receive high-quality and comfortable sports clothing for training and workouts.
3. Psychographics
Psychographic targeting goes further and examines the personality factors of the consumers; this involves looking at the psychological factors within consumer buying. Key factors include:
- Personality Traits: Consumer segmentation could be based on certain inherent characteristics, such as the consumers’ personality type, the degree of adventurous or cautious nature, etc. Hence, it would be easier to market the product based on certain consumer characteristics.
- Values and Beliefs: Environmental analysis helps brands to determine their clients’ values and beliefs, what people consider significant in their lives, and what they are willing to pay for – tradition, sustainability, innovation, and more.
- Attitudes and Opinions: Understanding the consumers’ perceptions towards several issues, such as technological advancement, social issues, and lifestyles, can help develop how such products are marketed.
- Motivations and Aspirations: Knowing what motivates consumers can be handy when creating a marketing campaign tied to their goals, whether success, freedom, creativity or belongingness.
- Fears and Challenges: When brands are aware of consumer fears and issues, they provide solutions that help create trust and, eventually, customers.
Example: A luxury car brand could appeal to someone who values status, speed, and class. Such consumers will likely be motivated by the need for achievement, esteem recognition, and status for the products they purchase to showcase these accomplishments.
4. Attitudes and Opinions
This type focuses on people’s views and beliefs about various topics:
- Political stances
- Social issues
- Environmental concerns
- Cultural preferences
- Brand perceptions
Example: If you are designing an organic cleaning product line, then the goodwill will probably appeal to those who are sensitive to environmental issues. They are open to such matters as the environmental impact, lowering the waste rate, and utilizing non-toxic and recyclable materials.
These attitudes can be summed up as follows: A brand can effectively advertise its products as non-hazardous to the environment by using natural, recyclable, and eco-friendly packaging and manufacturing processes.
The amortizations may stress the potential benefits of the correct choice of environmentally friendly cleaning products, appealing to customers’ values and their desire to change traditional cleaners to environmentally friendly ones. This alignment guarantees that the brand’s communication appeals target the consumer’s green aspects well.
5. Location
Geographic targeting considers where people live or work:
- Country
- Region or state
- City or town
- Urban vs. rural areas
- Climate zones
Example: Sunscreen makers could target their promotion to coastal areas and those with high UV intensity. For instance, they can go for residents and visitors of sunny states such as Florida or California. They could also do campaigns in areas of outside activities like in Miami and Los Angeles. In this way, they would be aware of the regional specifics and adjust the message to focus on protecting skin from the sun in such regions. In this way, their product ads will be closer to the ears and eyes of those audiences who are more likely to require and use sunscreen products more often.
6. Behavior
Behavioral targeting looks at how people interact with products or services:
- Purchasing habits
- Brand loyalty
- Usage patterns
- Decision-making processes
- Online vs. offline shopping preferences
Example: An e-commerce platform might employ a specific population that is identified with internet shoppers who embrace ease and reasonable prices.
7. Subculture
This type focuses on distinct groups within larger cultures
- Ethnic subgroups
- Religious communities
- Youth subcultures (e.g., skaters, gamers)
Example: Halal food might be aimed at the Muslim population that has certain restrictions when it comes to their food choices.
8. Income
Income-based targeting considers financial resources:
- Income brackets
- Disposable income
- Spending habits
- Financial priorities
Example: High income persons with lots of disposable income could be the key audience that a luxury watch brand sells to.
9. Geography
This type considers broader geographical factors:
- Continental regions
- National boundaries
- Cultural similarities across regions
Example: A travel agency can market travel to adventure lovers in North America and those wanting to travel to South East Asia.
10. Education
Educational targeting focuses on academic background:
- The highest level of education attained
- Field of study
- Ongoing educational pursuits
- Professional certifications
Example: An LMS audience might include people employed in organizations who wish to acquire more skills, which can only be done while studying online part-time.
11. Target Market
While similar to the target audience, this focuses more on the broader market segment:
- Industry sectors
- Business types (B2B vs. B2C)
- Market size and growth potential
Example: Software might target SMEs in the healthcare industry, which is a specific company market niche.
12. Age
Age-based targeting considers life stages and generational differences:
- Children and teens
- Young adults
- Middle-aged individuals
- Seniors
Example: An example of segmentation is a retirement planning service targeting adults between 50 and 65 who are planning how to live after they have stopped working.
13. Fans
This type targets enthusiasts or supporters of particular:
- Sports teams or athletes
- Celebrities or influencers
- Brands or products
- Entertainment franchises
Example: A sports memorabilia company’s target consumer group might include fans of professional sports teams.
14. Gender
Gender-based targeting considers:
- Traditional gender roles and expectations
- Gender-specific needs or preferences
- Gender identity and expression
Example: A cosmetics company’s market might be the people of all genders who use makeup and beauty products.
15. Personality
This type focuses on individual character traits:
- Extroversion vs. introversion
- Openness to experience
- Conscientiousness
- Agreeableness
- Neuroticism
Example: A personal development app might be relevant to a person who is reflective and desirous of being a better person.
16. Customers
This type targets existing customers or specific customer segments:
- Loyal customers
- One-time buyers
- High-value customers
- At-risk customers
Example: A Subscription service may or may not have the same methods for getting past subscribers to stick around versus regaining the unsubscribed users.
17. Interests
Interest-based targeting focuses on hobbies, passions, and areas of curiosity:
- Sports and Fitness
- Arts and Culture
- Technology and gadgets
- Travel and exploration
- Food and cooking
Example: The strategies that can be used to combine past users may or may not be the same strategies used to win back users who had earlier unsubscribed from a specific Subscription service.
18. Everyone
Interest-based targeting focuses on hobbies, passions, and areas of curiosity:
- Essential goods (e.g., basic food items)
- Universal services (e.g., utilities)
- Mass-market entertainment
Example: An example of mass communication is a campaign educating people on the necessity of washing hands that would cover the entire population of a country.
Realizing these different forms of target markets, business organizations can develop even more specific and efficient promotional plans and initiatives to communicate closely with the targeted consumer teams.
Importance of Defining Your Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is crucial for several reasons:
Focus and Efficiency
Lack of funds implies that identification of a particular audience is quite useful in that it ensures concentrated effort. Focusing on the right type of customers ensures that time and money are spent in the right place and are not wasted by methods that cover large masses of the population.
Identifying a niche target market simplifies the overall marketing efforts because all the marketing strategies devised are specific and effective in targeting the likely consumers. This genuinely targeted strategy helps you make better use of resources and increases the efficiency of campaigns, resulting in better outcomes and higher ROI.
Targeted Communication
Information about the target audience’s age, preference, and necessity ensures that the kind of communication is much more appropriate and relevant in the process. This specificity of communications promotes a given result because everybody in the audience wants to feel recognized and valued in the process, enhancing relations and communications with the brand.
Increased Sales and Conversions
Thus, the likelihood of turning a particular target market into consumers or patrons soars because one is literally addressing the audience’s needs. Because it is very specific to their wants and needs, it helps increase the desirability of your products or services and have better conversions.
Brand Resonance
Consequently, the target market will dictate the brand personality, which can be easily associated with the consumers, hence building a loyal consumer community. If the brand is the epitome of what the intended consumer group strives to be or achieve, the Group will retain loyal customers and will refer others to patronize the brand.
Competitive Advantage
Knowing your rivals’ target market less than you do is a major advantage because it gives you an opportunity to position your products, services and communications to meet consumers’ needs. Such a deep understanding helps develop the unique selling proposition that sets one’s brand apart from those of competitors and builds a loyal customer base.

How to Identify Your Target Audience
Identifying your target audience involves several steps:
1. Analyze Your Current Customer Base
- Look at your sales data: Who do you target for the repeat business? Demographic factors (age, gender, location, and income level) that define the target group is another important aspect. What products or services are likely to be bought by such a population?
- Conduct customer satisfaction surveys: This is a great opportunity to get your customers to explain why they chose your company over the others, what issues your clients solve with your product/service, and what they like or dislike about it.
- Analyze customer reviews and feedback: Listen to what people often say about your brand, especially on social media. Look for similarities and possible conclusions about their wants and choices.
This step assists you to realize who is already creating value from what you are feeling in the market.
2. Conduct Market Research
- Surveys: Create surveys to define its participants within a wider population – the potential customers. Engage the customers by asking questions regarding their issues, purchasing behaviour, and brands they support.
- Focus groups: Assemble a group of your target consumers to lead a focus group discussion on your product/service, the state of your industry and your competitors. This will allow you to make amendments, have a good discussion, and collect useful qualitative information.
- Industry reports: Read articles, papers, journals, and various research works to gain a broad knowledge of the current market trends, competitors, and target customer base in your niche.
Market research assists a business person in the market in looking beyond the existing clients and understanding the market environment.
3. Examine Competitors
- Identify your main competitors.
- Look at their brochures, advertisements, and posting content concerning their target market.
- Try to search for the lacks in their portfolios or the market sectors that can be un provided.
Thus, information about competitors’ target audiences allows for targeting a somewhat different audience or filling the gaps in existing audience needs.
4. Create Buyer Personas
- Gather all the information that you have collected in all the previous steps.
- Create clear dissections of your target markets. These profiles are Buyer Personas and should comprise Demographics, psychographics (interests, values, and lifestyle), pains, gains, and media usage.
- Relate your personas with different names and interesting stories, as this will help you navigate the creative process of creating personas.
Buyer personas give you a clear picture of the specific customer you are targeting and the message you want to pass on or provoke in this customer.
5. Use Analytics Tools
- Analyze the experience visitors have on your website using tools such as Google Analytics to determine the demographic background of users, things that interest them and how they behave when on your website.
- Employ all the analytics tools available on social media platforms such as Facebook and Instagram to discover who interacts with you on those useful platforms.
Other digital measurements help identify who is already engaging with the organization’s online presence, which in turn helps to clarify the targeting of potential consumers.
6. Test and Refine
- Understand that you do not have to perfect everything at the initial stage of the realization process. Create marketing strategies that are informed by your idea of your target audience.
- Oversee the status of the campaigns you have and assess the outcome.
- Are you touching the right people? Are your messages resonating?
- Always be ready to flex your target audience and the messages you want to convey based on the findings.
Targeting is not a one-time activity. Repeat the procedures to increase your chances of finding the appropriate population for your message.
Target Audience Examples Across Industries

Let’s explore some specific target audience examples across various industries:
Technology Industry
Example 1: Smartphone Manufacturer
- Target Audience: Tech-savvy millennials aged 25-40
- Characteristics:
- Organizations that are at the forefront of adopting new technology
- Take pride in exclusive features and the product design
- Active on social media
- Capable of paying a higher cost for better tablets
Example 2: Educational Technology Company
- Target Audience: K-12 school administrators & teachers
- Characteristics:
- Seeking innovative learning solutions
- Budget-conscious
- Concentrating on the patterns of students’ attitudes and achievements
- Seeking information on continuing education

Fashion Industry
Example 1: Sustainable Fashion Brand
- Target Audience: Sustainable women of working-age group 25-45 years.
- Characteristics:
- Preferentially, buy ethical and sustainable goods.
- Inclined towards products that cost slightly more if they contribute to the environment.
- Active in environmental causes
- Both prefer quality clothes in their wardrobes more than they do the quantity.
Example 2: Luxury Accessories Brand
- Target Audience: High-income professionals aged 35-60
- Characteristics:
- Value status and exclusivity
- Appreciate fine craftsmanship
- Frequent travellers
- Attend high-profile social events

Food and Beverage Industry
Example 1: Organic Snack Food Company
- Target Audience: Health-conscious parents aged 30-45
- Characteristics:
- Ensure that the meals provided by the family have nutritional value.
- Get good, enjoyable snacks. Organization of snacks is important
- Ready to purchase the organic product at a higher price.
- Modern people actively engage in different activities and tight schedules.
Example 2: Craft Beer Brewery
- Target Audience: Beer enthusiasts aged 25-40
- Characteristics:
- Value the specialty of the taste and the process of making the beverages.
- Love to experiment with new and regional products.
- Alcoholic beverage consumers who regularly participate in beer fests or beer-tasting events.
- Value authenticity and craftsmanship

Financial Services Industry
Example 1: Online Investment Platform
- Target Audience: Millennial professionals aged 25-40
- Characteristics:
- Able to use technology and adequate with technology-initiated financial services.
- Looking for a way to grow wealth over the long term
- Transparency of values and very affordable fees
- Prefer self-directed investment options
Example 2: Retirement Planning Service
- Target Audience: Baby Boomers aged 55-70
- Characteristics:
- Young pre-retirees or those within a year or two of retiring
- Another unique feature is the fear of being financially vulnerable in the future
- Primarily in fields like estate planning and transfer of wealth
- May be caring for ageing parents or an adult child

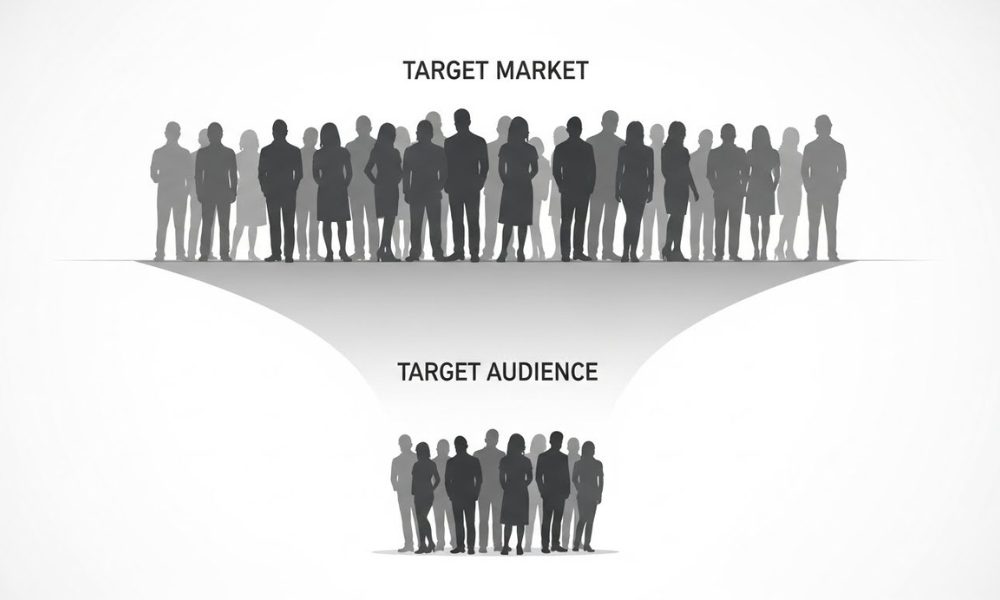
Target Market and Its Relation to Target Audience
Targeting audience and target market are interrelated concepts, but they are unique for differentiation in marketing strategy. A target market can be defined as a specific segment of the population to which organizations direct their goods and services. This group is generally more extensive and encompasses the whole population category that would be able to buy a certain product or use a particular service. For example, target consumers for a company dealing in organic baby food can be parents of babies. This large and generalized population can be segmented in many subcategories in terms of perception.
The target market concept is at the root of further narrowing down the target consumer group. However, while a target market defines the area and the demography of the population, the target audience goes deeper into the psychographic and behavioristic approaches. This involves identifying a consumer’s beliefs and perceptions towards a product or service, wants, needs and behavior patterns within the marketer’s chosen market segment. For instance, whereas organic baby food fits into the segment of parents with infants, its target consumers are young mothers aged 25-35 years within urban centers concerned with their health and the environment. This is because the type of segmentation that is being used in the current approach means getting a better understanding of the target market’s needs, as well as analyzing the behavioural patterns of the audience, which in turn helps marketers to design better campaigns and messages which can be incredibly effective for breaking through the clutter.
The recognition of the target market and target audience thus helps businesses formulate effective marketing strategies. In the next step, the identified broad target market is further segmented to discover which segments are responsive to the company’s intended message. This includes the choice of messages to provide, the proper channels to appeal to the segments reached, and the creation of campaigns that are particularly relevant to the identified segments. Because the audience is heterogeneous, companies can increase their interest and improve the conversion results by focusing on the unique characteristics of the target population.
Conclusion
These concepts of ‘market segmentation’ and ‘marketing target’ are vital to formulating and implementing a profitable marketing plan and a growing business. Demographics, psychographics, behaviours and all the other parameters need to be studied in depth to generate a clear picture of the target customers. Your products, services, and marketing to the target audience can be well towards achieving the appropriate goal and enhancing patronage and consumer satisfaction, which will result in good sales and overall organizational growth.
It is important to note that target audiences are dynamic and can be further modified by technology, society, and consumers themselves. Thus, you must occasionally reevaluate and update your target audience definition to maintain the business’s competitiveness in the current marketplace.
With the knowledge of the different target audiences explained in this guide and the understanding of their place in the overall target market, you are well prepared to identify, comprehend, and then simply reach your target clientele. This fundamental concept paves the way to promoting effective and efficient marketing strategies that would have the right impact on your audience and on what you want to sell.






